1. Read the title of the text. Guess what this text is about (write down 5-8 sentences; use topical vocabulary)
What do we know about environmental problems?
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants. Pollutants can be natural and they can also be created by human activity.
Many things that are useful to people produce pollution. Cars spew pollutants from their exhaust pipes. Burning coal to create electricity pollutes the air. Industries and homes generate garbage and sewage that can pollute the land and water. Pesticides-chemical poisons used to kill weeds and insects-seep into waterways and harm wildlife.
Air Pollution
Factory smoke stack polluting the air with emissions.
According to the dictionary, air pollution is the contamination of air by smoke and harmful gases, mainly oxides of carbon, sulphur, and nitrogen.
Some examples of air pollution include: exhaust fumes from vehicles; the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil or gas; harmful off-gasing from things such as paint, plastic production and so on; radiation spills or nuclear accidents; air pollution is linked to asthma, allergies and other respiratory illnesses. You can more about how the environment affects human health here.
Land Pollution
Land pollution is the degradation of the Earth's surface caused by a misuse of resources and improper disposal of waste. Some examples of land pollution include: litter found on the side of the road; illegal dumping in natural habitats; oil spills that happen inland; the use of pesticides and other farming chemicals; damage and debris caused from unsustainable mining and logging practices; radiation spills or nuclear accidents.
Land pollution is responsible for damage done to natural habitat of animals, deforestation and damage done to natural resources, and the general uglying up of our communities.
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution is any loud sounds that are either harmful or annoying to humans and animals. Some examples of noise pollution: construction or demolition noise; human activities such as sporting events or concerts. Noise pollution is disruptive to humans' stress levels, may be harmful to unborn babies, and drives animals away, causing nervousness and decreasing their ability to hear prey or predators.
Thermal Pollution
Thermal pollution is the increase of temperature caused by human activity. For example: warmer lake water from nearby manufacturing (using cool water to cool the plant and then pump it back into the lake); included in thermal pollution should also be the increase in temperatures in areas with lots of concrete or vehicles, generally in cities.
These kinds of environmental pollution can cause aquatic life to suffer or die due to the increased temperature, can cause discomfort to communities dealing with higher temperatures and can even affect plant-life in and around the area.
Water Pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of any body of water (lakes, groundwater, oceans, etc).
Some examples of water pollution: raw sewage running into lake or streams; industrial waste spills contaminating groundwater; radiation spills or nuclear accidents; illegal dumping of substances, or items in bodies of water; biological contamination, such as bacteria growth; these kinds of environmental pollution are linked to health issues in humans, animals and plant-life.
2. Write down words from the topical vocabulary including those you have come across while reading the text which can help you to discuss the following issues:
-
Air pollution
-
Greenhouse effect
-
Land pollution
-
Deforestation
-
Water pollution
-
Noise pollution
-
Thermal Pollution
3. Suggest the solution of each problem given using the words from the text:
-
contamination
-
gas
-
pollution
-
chemicals
-
light pollution
-
a substance used in chemistry or produced by a process involving chemistry
-
the effect of too much artificial light at night, which prevents people from seeing the night sky properly and may affect the natural rhythms of living things
-
the introduction of harmful materials into the environment
-
a substance such as air that is neither a solid nor a liquid
-
the process of making something dirty, polluted, or poisonous by adding a chemical, waste, or infection
4. Complete the sentences using the text:
-
Harmful materials which damage the environment are called _______________ .
-
Cars __________________ pollutants from their exhaust pipes.
-
Air pollution is the contamination of air by smoke and harmful gases, mainly _________________ .
-
Some examples of land pollution include the use of ______________ and other farming chemicals.
-
Land pollution is responsible for damage done to natural habitat of animals, _____________ and damage done to natural resources.
-
Construction or ________________ noise is a common example of noise pollution.
-
______________ is the increase of temperature caused by human activity.
-
Industrial ____________________ contaminate groundwater.
-
Water pollution is the __________________ of any body of water.
-
________________ running into lake or streams poisons fish.
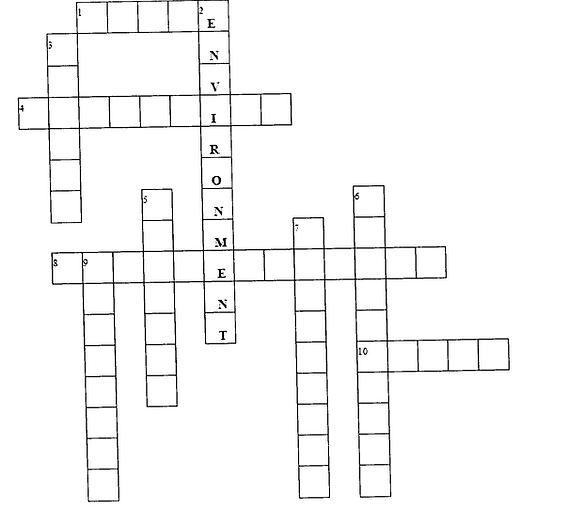
5. Do the crossword
Across
1. A material or substance which is eliminated or discarded as no longer useful or required after the completion of a process.
4. the introduction of harmful materials into the environment
8. Cutting down and clearing areas of forest.
10. Poisonous
Down
2. The air, water and land in or on which people, animals and plants live.
3. The vaporous system made up of small particles of carbonaceous matter in the air, resulting mainly from the burning of organic material, such as wood or coal
5. A prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall, leading to a shortage of water.
6. The weather conditions generally present in an area or over a long period.
7. A gradual rise in the world's temperatures caused by polluting gases such as carbon dioxide which are collecting in the air around the Earth and preventing heat escaping into space.
9. The production and discharge of something.